Guide to Stainless Steel Sheet Welding
What is Stainless Steel Sheet?
Stainless steel sheet is a metalsheet made of stainless steel, a steel alloy containing at least 10.5% chromium. This high chromium content gives stainless steel corrosion-resistant properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Stainless steel plates have smooth surfaces, high plasticity, toughness and mechanical strength, and have strong corrosion resistance to acids, alkaline gases, solutions and other media. It is alloy steel that does not rust easily. Stainless steel sheets are available in a variety of thicknesses and sizes and are used in industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace and manufacturing. They are commonly used for countertops, backsplashes, kitchen appliances, decorative purposes, and as structural components of buildings.
Welding stainless steel requires specific techniques and considerations due to the unique properties of the material. Here are some guide to help you welding stainless steel sheet:
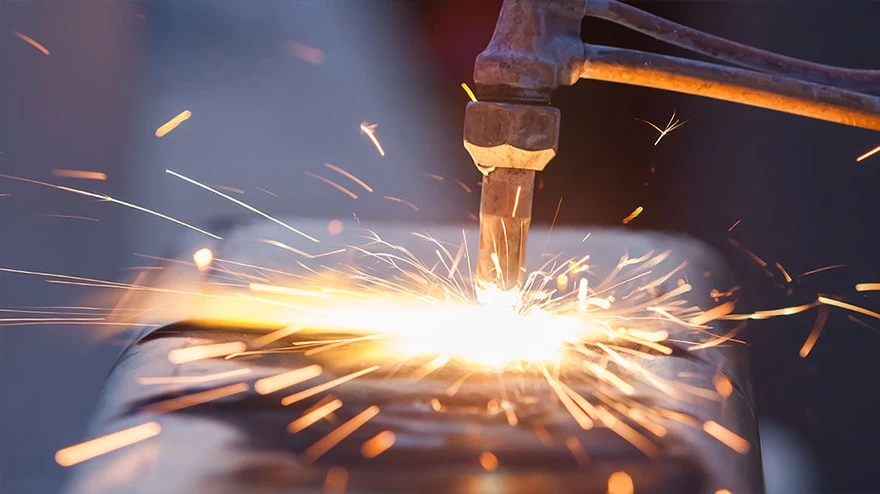

Guide to Stainless Steel Sheet Welding
1. Welding is a very dangerous process. In fact, no matter what material is welded, you need to wear protective equipment before welding, such as welding gloves, welding helmets and welding aprons. The welding environment is also very important, ensuring a ventilated working environment.
2. Before welding stainless steel sheet, be sure to clean the surface of the plates to remove any dirt, oil, or contaminants. Any oxide or scale can be removed using a stainless steel scrub brush or a grinder with a wire brush attachment. Keeping the surface of stainless steel plates clean is also very important for welding.
3. Select filling materials that match the composition of the stainless steel plate. Common filler materials for stainless steel welding include ER308, ER309 or ER316. Consult the manufacturer's recommendations or a welding expert to determine the appropriate filler material for your specific stainless steel grade.
4. Set up your welding equipment: Use a TIG (tungsten inert gas) or MIG (metal inert gas) welder, depending on your preference and skill level. Make sure your machine is set to the correct amperage and voltage settings for the thickness of the stainless steel sheet.
5. Prepare the joint: Determine the type of joint to be welded, such as a butt joint, lap joint, or T-joint. If necessary, use clamps or magnets to hold the board in place. If necessary, the edges of the board can be beveled to create a V-groove or U-groove joint, providing better penetration and strength.
6. Spot weld the plates: Use small spot welds to temporarily hold the plates together. This will prevent any movement during welding.
7. Start welding: Start welding from one end of the joint and move smoothly along the joint in a controlled manner. Maintain a consistent speed of travel to ensure proper blending and penetration. Use the correct welding technique for your chosen process (TIG or MIG) and filler material.
8. Control heat input: Stainless steel is prone to deformation and warping due to its low thermal conductivity. To minimize these problems, reduce heat input by reducing amperage and increasing travel speed. This will help prevent excess heat from building up in the material.
9. Backpurge (optional): If the welded joint requires corrosion resistance on both sides, you can consider using backpurge technology. This involves using an inert gas, such as argon, to purge the backside of the joint during the welding process. This helps prevent oxidation and ensures the weld is clean and corrosion-resistant.
10. Post-welding treatment: After welding is completed, use a stainless steel wire brush to remove welding slag or discoloration. Clean the welded area with a stainless steel cleaner or solvent to remove any remaining contaminants.
11. Check the welds: Check the welded joints for defects such as cracks, pores, or lack of fusion. Use non-destructive testing methods such as visual inspection, color penetrant testing or radiographic testing to ensure weld quality.
Keep in mind that welding stainless steel requires practice and experience to achieve a quality weld. We are a manufacturer of welding stainless steel sheet in China. We have very rich experience in welding stainless steel sheets and have completed many welded stainless steel sheet projects of different sizes. We are a very trustworthy supplier. If you are looking for such a reliable welded stainless steel manufacturer, please contact us.